How Hunger and Poverty are Nigeria’s Major Barriers to Peace and Stability
How Hunger and Poverty are Nigeria’s Major Barriers to Peace and Stability

President Bola Ahmed Tinubu
In Nigeria, the twin challenges of hunger and poverty continue to pose significant obstacles to achieving lasting peace and stability. Despite ongoing efforts by the government and various organizations, these issues remain deeply entrenched, contributing to a range of social, economic, and political problems.
Poverty, which affects a substantial portion of the population, has led to widespread inequality and discontent. Many Nigerians struggle with limited access to basic necessities such as food, healthcare, and education. This dire situation exacerbates feelings of frustration, fueling unrest and increasing vulnerability to extremist ideologies and violent conflicts.
Hunger, too, is a critical issue. According to reports, millions of Nigerians face food insecurity, with access to adequate nutrition being a challenge for many, especially in rural areas. The combination of poverty and hunger is a fertile ground for social instability, as people are often forced to resort to desperate measures to survive.
These issues are not only affecting individuals but are also destabilizing entire regions. Areas plagued by high levels of poverty and food insecurity are often more susceptible to violence, insurgency, and displacement. The ongoing insurgency in the northeast, for example, is partly driven by socio-economic deprivation, with vulnerable communities being easy targets for radicalization.
To achieve lasting peace in Nigeria, experts argue that addressing the root causes of hunger and poverty is essential. Sustainable economic policies, increased investment in rural development, and efforts to improve food security are critical to reducing the vulnerability of the population to conflict and promoting social cohesion.
TRENDING SONGS
 NNPC Boss Ojulari Bags UK Energy Institute Fellowship
NNPC Boss Ojulari Bags UK Energy Institute Fellowship
 Shock in Anambra: Bride Disappears Moments Before Wedding
Shock in Anambra: Bride Disappears Moments Before Wedding
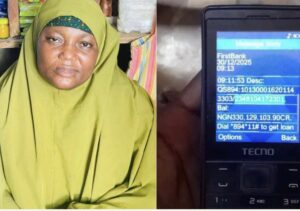 Nigerian Woman Returns ₦330 Million Accidentally Credited to Her Account
Nigerian Woman Returns ₦330 Million Accidentally Credited to Her Account
 APC Don Reach Morocco?’ VeryDarkMan Reacts to Seyi Tinubu Poster
APC Don Reach Morocco?’ VeryDarkMan Reacts to Seyi Tinubu Poster
 Bride Breaks Down in Tears as Wedding Meals Were Kept Secretly While Guests Go Home Hungry
Bride Breaks Down in Tears as Wedding Meals Were Kept Secretly While Guests Go Home Hungry
 Odogwu by Day, Robber by Night: How Marriage Joy Turned Into Tragedy
Odogwu by Day, Robber by Night: How Marriage Joy Turned Into Tragedy
 Nigerian Officials Allegedly Pocket N4–6B Weekly Through Smuggling Cartels at Seme–Badagry Border
Nigerian Officials Allegedly Pocket N4–6B Weekly Through Smuggling Cartels at Seme–Badagry Border
 Ahmad Yerima: Naval Officer to Face No Sanctions After Clash with Wike – Matawalle
Ahmad Yerima: Naval Officer to Face No Sanctions After Clash with Wike – Matawalle
 Trending Video: Muslim Man Joins Wife in Hallelujah Challenge ‘Dress Like Your Miracle’ Night
Trending Video: Muslim Man Joins Wife in Hallelujah Challenge ‘Dress Like Your Miracle’ Night
 Woman Seeks Advice as Late Brother’s Wife Refuses to Mourn Him Following His Death With Alleged Mistress
Woman Seeks Advice as Late Brother’s Wife Refuses to Mourn Him Following His Death With Alleged Mistress
Share this post with your friends on ![]()













