Five Essential Steps to Prevent Cholera
Five Essential Steps to Prevent Cholera
In light of the cholera outbreak declared in Lagos on June 15, 2024, by Nigerian health authorities, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported 436 suspected cases within just six days, with the number rising to over 500, including 43 confirmed cases and a 5.4% case fatality rate among suspected cases.
The situation continues to escalate, with the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) documenting 53 cholera-related deaths and 1,528 suspected cases across 31 states and 107 local government areas as of June 24, 2024, resulting in a 3.5% case fatality rate for the year.
Globally, cholera affects between 1.3 to 4.0 million people annually, leading to 21,000 to 143,000 deaths, mostly among those with mild or asymptomatic cases who can be effectively treated with oral rehydration solutions.
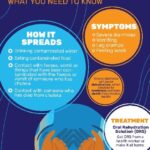
Given the outbreak’s spread, particularly in crowded areas and prisons, public health education on cholera prevention is critical. During a recent health awareness event, Dr. Oche Otorkpa, a public health expert and Executive Director of Public Health Nigeria, emphasized the importance of maintaining hygienic practices to prevent cholera. He outlined five essential practices:
1. Practice Good Hygiene**: Regularly wash hands with soap and clean water, especially before handling food, after using the toilet, and after caring for cholera patients. Use hand sanitizers if soap and water are unavailable.
2. Ensure Safe Water and Food**: Consume only safe water that has been boiled, treated, or chlorinated. Avoid raw or undercooked seafood, and thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables before consumption. Refrain from purchasing snacks and foods from unhygienic street vendors.
3. Maintain Sanitary Conditions**: Properly dispose of human waste to prevent contamination of water sources. Use latrines or toilets and avoid open defecation. Keep living and cooking areas clean.
4. Promote Community Awareness**: Educate family and community members about cholera symptoms, such as severe diarrhea and vomiting, and encourage prompt medical care if symptoms occur.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals and communities can significantly reduce their risk of contracting cholera and aid health authorities in controlling outbreaks.
TRENDING SONGS
 NPMA Appeals to Nigerian Government for Compensation After Lagos Market Fire
NPMA Appeals to Nigerian Government for Compensation After Lagos Market Fire
 Rest Every Four Hours, FRSC Issues Safety Guide for Fasting Motorists
Rest Every Four Hours, FRSC Issues Safety Guide for Fasting Motorists
 NNPC Boss Ojulari Bags UK Energy Institute Fellowship
NNPC Boss Ojulari Bags UK Energy Institute Fellowship
 Shock in Anambra: Bride Disappears Moments Before Wedding
Shock in Anambra: Bride Disappears Moments Before Wedding
 Nigerian Woman Returns ₦330 Million Accidentally Credited to Her Account
Nigerian Woman Returns ₦330 Million Accidentally Credited to Her Account
 APC Don Reach Morocco?’ VeryDarkMan Reacts to Seyi Tinubu Poster
APC Don Reach Morocco?’ VeryDarkMan Reacts to Seyi Tinubu Poster
 Bride Breaks Down in Tears as Wedding Meals Were Kept Secretly While Guests Go Home Hungry
Bride Breaks Down in Tears as Wedding Meals Were Kept Secretly While Guests Go Home Hungry
 Odogwu by Day, Robber by Night: How Marriage Joy Turned Into Tragedy
Odogwu by Day, Robber by Night: How Marriage Joy Turned Into Tragedy
 Nigerian Officials Allegedly Pocket N4–6B Weekly Through Smuggling Cartels at Seme–Badagry Border
Nigerian Officials Allegedly Pocket N4–6B Weekly Through Smuggling Cartels at Seme–Badagry Border
 Ahmad Yerima: Naval Officer to Face No Sanctions After Clash with Wike – Matawalle
Ahmad Yerima: Naval Officer to Face No Sanctions After Clash with Wike – Matawalle
Share this post with your friends on ![]()













